Numeric Python (NumPy): in Python
NumPy is a Python library. NumPy is used for working with arrays.
It is also used in linear algebra and matrices.
Use of NumPy:
In Python lists serve the purpose of arrays, but they are slow to process.
It provides an array object that is faster than Python lists which is called ndarray.
NumPy arrays are stored at one continuous place in memory so processes can access and manipulate them very efficiently.
Importing NumPy:
Once NumPy is installed, import it by adding the import keyword:
Syntax: import numpy
Creating Object:
We can create a NumPy ndarray object by using the array()function.
Converting a list to array using array() function.
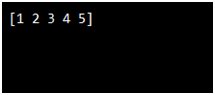
Example:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(ar)
Output
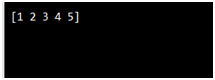
Use a tuple to create a NumPy array:
Converting tuple to array using array() function.
Example:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array((1, 2, 3, 4, 5))
print(ar)
Output
Dimensions in Arrays
0-D Arrays
0-D arrays are the elements in an array. Each value in an array is a 0-D array.
Example 0-D array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array(42)
print(ar)
Output

1-D Arrays:
A One-Dimensional Array is the simplest form of an Array in which the elements are stored linearly. These are the most common and basic arrays.
Example of 1-D array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(ar)
Output
2-D Arrays
2D array can be defined as an array of arrays. The 2D array is organized as matrices which can be represented as the collection of rows and columns. These are often used to represent matrix. NumPy has a whole sub module dedicated towards matrix operations called numpy.mat
Example of a 2-D array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(ar)
Output

3-D arrays:
A 3D array is a multi-dimensional array(array of arrays). A 3D array is a collection of 2D arrays.
Example of 3-D array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]])
print(ar)
Output

How to Check Number of Dimensions?
To check the number of dimensions of an array, we can use ndim attribute.
ndim attribute returns an integer that tells us how many dimensions the array have.
Example of ndim attribute:
import numpy as np
a = np.array(42)
b = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(a.ndim)
print(b.ndim)
Output

Access Array Elements:
You can access an array element by referring to its index number.
Example of accessing the elements in an array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(ar[0])
Output

Access 2-D Arrays
To access the elements from a 2-D array we can use comma separated integers representing the dimension and the index of the element.
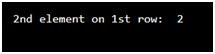
Example to access elements of 2-D array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([[1,2,3,4,5], [6,7,8,9,10]])
print('2nd element on 1st row: ', ar[0, 1])
Output
Access 3-D Arrays
To access the elements from a 3-D array we can use comma separated integers representing the dimensions and the index of the element.
Example to access the elements from 3-D array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]])
print(ar[0, 1, 2])
Output

Data Types in NumPy:
NumPy has some extra data types, and refer to data types with one character.
Below is a list of all data types in NumPy and the characters used to represent them.
- i - integer
- b - boolean
- u - unsigned integer
- f - float
- c - complex float
- m - timedelta
- M - datetime
- O - object
- S - string
- U - unicode string
- V - fixed chunk of memory for other type ( void )
Checking the Data Type of an Array:
We can check the data type of an array using dtype.
dtype returns the data type of the array:
Example to check the data type of an array:
import numpy as n
ar = n.array([4, 8, 2, 7])
print(ar.dtype)
Output

Creating Arrays With a Defined Data Type:
We can also create a new array with pre defined data type using the dtype as an argument.
array() function can take an optional argument: dtype that allows us to define the expected data type of the array elements:
Example:
import numpy as n
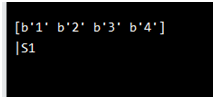
ar = n.array([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype='S')
print(ar)
print(ar.dtype)
Output
Converting Data Type on Existing Arrays:
The best way to change the data type of an existing array, is to make a copy of the array with the astype() method.
The data type can be specified using a string.
Example:
We can change the data type from float to integer by using 'i' as parameter value:
import numpy as n
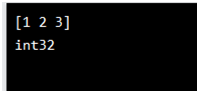
ar= n.array([1.1, 2.1, 3.1])
newar = ar.astype('i')
print(newar)
print(newar.dtype)
Output
In same way we can convert the data types from 1 type to another if the data type supports conversion to that data type:
Example:
We can convert data type from int to bool.
import numpy as np
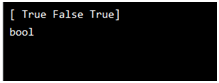
arr = np.array([1, 0, 3])
newarr = arr.astype(bool)
print(newarr)
print(newarr.dtype)
Output
The Difference Between Copy and View:
The main difference between a copy and a view of an array is that the copy is a new array, and the view is just a view of the original array.
COPY:
Example:
Make a copy of the original array, change value from original array and display both arrays:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x = arr.copy()
arr[0] = 42
print(arr)
print(x)
Output

The value from original array changes but the values of the new copied array remains the same.
VIEW:
Example
Make a view of the original array, change the value from original array and display both arrays:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
x = arr.view()
arr[0] = 42
print(arr)
print(x)
Output

The value from both the arrays change when view is used.
Searching Arrays:
You can search an array for a certain value. To search an array, use the where() method.
Example to search the array for a certain value:
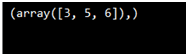
import numpy as p
ar = p.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 4])
x = p.where(ar == 4)
print(x)
Output
Search Sorted Method:
To perform a binary search in array, we can use the searchsorted() method.
Example:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([6, 7, 8, 9])
x = np.searchsorted(arr, 7)
print(x)
Output

Search array from the Right Side:
By default the left most index is returned, but we can give side='right' to return the right most index instead.
Example:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([6, 7, 8, 9])
x = np.searchsorted(arr, 7, side='right')
print(x)
Output
Search Multiple Values:
To search for more than one value, use an array with the specified values.
Example
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 3, 5, 7])
x = np.searchsorted(arr, [2, 4, 6])
print(x)
Output

Sorting Arrays:
Sorting means putting elements in an ordered sequence.
We can sort an array in numpy using the sort() function.
Example:
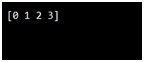
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([3, 2, 0, 1])
print(np.sort(arr))
Output
Sorting a 2-D Array:
When you use the sort() method on a 2-D array, both arrays will be sorted:
Example:
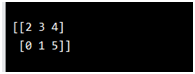
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[3, 2, 4], [5, 0, 1]])
print(np.sort(arr))
Output
Filtering Arrays:
Getting some filtered elements out of an existing array.
In NumPy, you can filter an array using a boolean index list.
Example:
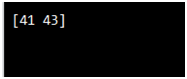
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([41, 42, 43, 44])
x = [True, False, True, False]
newarr = arr[x]
print(newarr)
Output
Creating the Filter Array:
We can also create a new filtered array using conditions.
Example
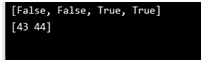
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([41, 42, 43, 44])
filter_arr = []
for element in arr:
if element > 42:
filter_arr.append(True)
else:
filter_arr.append(False)
newarr = arr[filter_arr]
print(filter_arr)
print(newarr)
Output
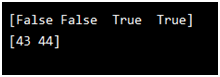
Creating Filter Directly From Array:
We can substitute the array in our condition.
Example
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([41, 42, 43, 44])
filter_arr = arr > 42
newarr = arr[filter_arr]
print(filter_arr)
print(newarr)
Output